WaterJet Technology
 |
||||
|
History
In the 1950s, forestry engineer Norman Franz experimented
with an early form of water jet cutter to cut
lumber.
However, the technology did not advance notably until the
1970s when
Mohamed Hashish
created a technique to add abrasives to the water jet
cutter. This and other concepts allowed
Yih-Ho Michael Pao
to develop commercial "ultrahigh-pressure WaterJets and
abrasive-WaterJets into better tools for industrial cutting,
drilling, and milling, especially for the flexible factory
automation." Today the water jet is unparalleled in many
aspects of cutting and has changed the way many products are
manufactured. Many types of water jets exist today,
including plain water jets, abrasive water jets, percussive
water jets,
cavitation
jets and hybrid jets.
Operation
The cutter is commonly connected to a high-pressure
water pump where the water is then ejected from the nozzle,
cutting through the material by spraying it with the jet of
high-speed water. Additives in the form of suspended grit or
other abrasives, such as
garnet
and
aluminum oxide,
can assist in this process. |
||||
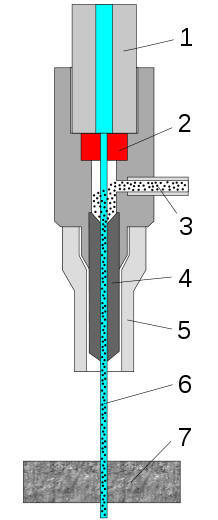
A diagram of a water jet cutter: |
||||
More |
||||
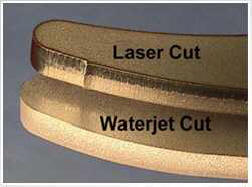
| In addition to no heat-affected
zone, the benefits and applications for WaterJet technology
are limitless and ever-expanding. In comparison to other
cutting technologies: |
||||
| WaterJet | Plasma | Laser | EDM | |
| Process | Erosion
process: high speed liquid sandpaper |
Burning /
melting process using high temperature ionized gas arc |
Melting
process using concentrated laser light beam |
Erosion
process using electrical discharge |
| Materials |
Any material. |
Primarily steel, |
Primarily steel, stainless and aluminum. Can also cut a variety of other materials. |
Conductive |
| Thickness |
Up to 24 inches, Z constraint |
Up to 2-3
inches, depending on material. |
Generally 1 inch |
Generally 12 |
|
Part Accuracy |
Up to .001" |
Up to .010" |
Up to .001" |
Up to .0001" |
|
Machine Setup |
Same setup |
Same setup |
Different |
Different wire types for different jobs |
|
As the grid above illustrates - WaterJet cutting technology has clear advantages over other cutting methods. |
||||








